Microsoft Research333 тыс
Опубликовано 8 февраля 2018, 20:17
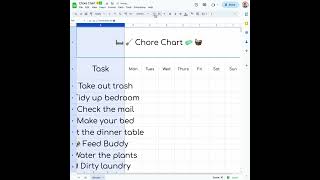
Protecting huge amounts of data stored in the cloud from server crashes resulted in distributed storage systems transitioning to erasure coding based schemes. Local Reconstruction Codes (LRCs) have emerged as the codes of choice for these applications. They allow super fast recovery in the typical case of a small number of crashes by reading only a few number of healthy servers (called 'locality'), while still protecting the data from the unlikely event of a large number of crashes. They have many good properties of simply replicating data while being much more storage efficient and crash resilient. Maximally Recoverable LRCs (MR LRCs) are the information theoretically the most optimal LRCs; they can recover from every feasible crash scenario for a given storage efficiency and locality. MR LRCs have already been deployed in Microsoft Azure storage system and other Windows storage systems to great acclaim, outperforming traditional erasure coding systems. Designing such codes over small finite fields is crucial for applications. Unfortunately, we are far from having an understanding of the minimal field size required for these codes. In this talk, we will present our progress on LR MRCs. We prove the first polynomially growing lower bounds on field size for MR LRCs using an interesting connection to incidence geometry, prior to our work no super linear lower bounds were known. We also present some linear field size MR LRC constructions in some parameter ranges which are very relevant in practice.
See more at microsoft.com/en-us/research/v...
See more at microsoft.com/en-us/research/v...
Свежие видео
Случайные видео